Embarking on the path to mental well-being necessitates navigating a myriad of therapeutic approaches, each offering distinct strengths. Within this spectrum, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) counseling emerges as a beacon of transformative potential. In our exploration of CBT’s intricacies, our objective is to illuminate its efficacy and assist you in discerning its alignment with your journey towards personal growth and mental health.
CBT’s spotlight on the interplay between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors sets it apart, providing a structured and goal-oriented framework. By unraveling its layers, we invite you to consider whether CBT could be the catalyst for positive change in your life, guiding you towards a more profound understanding of self and the tools to navigate the complexities of the human mind.
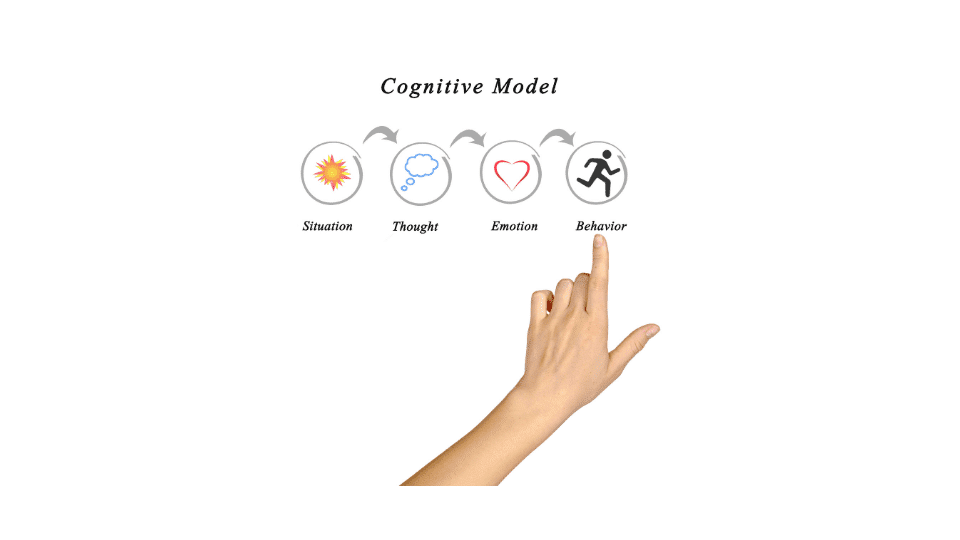
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a widely recognized and evidence-based form of psychotherapy that focuses on the interplay between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Unlike traditional therapeutic approaches, CBT is present-focused and problem-oriented, aiming to identify and modify unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors contributing to emotional distress.
CBT operates on the premise that our thoughts influence our feelings and behaviors, creating a cycle that can either perpetuate negative patterns or be redirected towards positive change. Through collaboration between the therapist and the individual, CBT seeks to uncover and challenge distorted thinking, fostering healthier perceptions and coping mechanisms.
The Core Principles of CBT
1. Cognitive Restructuring
One of the foundational principles of CBT is cognitive restructuring, which involves examining and challenging negative thought patterns. This process helps individuals identify automatic thoughts and cognitive distortions that contribute to anxiety, depression, or other emotional struggles. By replacing these negative cognitions with more balanced and realistic ones, individuals can experience a shift in their emotional well-being.
2. Behavioral Activation
Behavioral activation is another key element of CBT, emphasizing the connection between thoughts and actions. Through this approach, individuals learn to engage in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment, countering the impact of low mood or depression. By gradually increasing positive behaviors, individuals can disrupt the cycle of negative thinking and reinforce a more positive outlook on life.
3. Exposure Therapy
For those grappling with anxiety disorders, exposure therapy is a potent component of CBT. This technique involves gradually and safely facing feared situations or stimuli, helping individuals confront and overcome their anxieties. Through systematic desensitization, individuals learn to manage and reduce their anxiety responses, empowering them to navigate the challenges they once found overwhelming.
The Collaborative Therapeutic Relationship
A distinctive feature of CBT is the collaborative nature of the therapeutic relationship. Therapists and clients work together as active partners in the process of change. The therapist provides guidance, support, and expertise in CBT techniques, while the individual contributes their unique insights and experiences. This partnership fosters a sense of empowerment and ownership, enhancing the effectiveness of the therapeutic journey.
Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for You?
1. Goal-Oriented Approach
If you prefer a structured and goal-oriented approach to therapy, CBT may align well with your preferences. The focus on specific, measurable goals allows individuals to track their progress and celebrate achievements, creating a sense of momentum in the therapeutic process.
2. Active Participation
CBT requires active participation from individuals. If you are willing to engage in self-reflection, homework assignments, and the implementation of new coping strategies between sessions, CBT may be a fitting choice. The commitment to practicing new skills in daily life enhances the effectiveness of the therapy.
3. Preference For Present-Focused Solutions
CBT is particularly beneficial for those seeking solutions to current challenges. If you are more interested in addressing the here and now rather than delving extensively into past experiences, CBT’s present-focused approach may resonate with your therapeutic goals.
4. Openness To Change
Embracing change is a fundamental aspect of CBT. If you are open to exploring and modifying entrenched thought patterns and behaviors, CBT can provide you with the tools to create lasting positive change. The willingness to challenge and reframe long-standing beliefs is a crucial factor in the success of CBT.

Potential Considerations
While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is highly effective for many individuals, it may not be the best fit for everyone. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
1. Complex Trauma
Individuals with a history of complex trauma or deep-seated issues stemming from early life experiences may benefit from therapeutic modalities that explore the roots of these challenges in greater depth. While CBT can still be a valuable component, a more integrative and comprehensive approach may be warranted.
2. Preference For Insight-Oriented Therapy
If you are drawn to therapy that delves extensively into exploring and gaining insights into your past, traditional psychodynamic or psychoanalytic approaches might be more suitable. These modalities focus on uncovering the underlying causes of emotional struggles, offering a different path to self-discovery.
3. Need For Long-Term Support
CBT is often designed as a relatively short-term therapeutic intervention, with a focus on equipping individuals with practical skills to manage current challenges. If you require long-term support or have ongoing mental health concerns, discussing the duration and structure of therapy with your therapist is crucial.
Conclusion
Embarking on the therapeutic journey of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an opportunity for profound personal growth and emotional resilience. The transformative force of CBT is rooted in its practical strategies, collaborative approach, and goal-oriented focus.
As you contemplate this path, reflect on your preferences, articulate your goals, and assess your openness to change. The true power of CBT extends beyond its evidence-based techniques; it thrives in the synergy forged between therapist and individual. Together, they navigate the intricacies of thought patterns and behaviors, steering towards lasting positive change.
Whether CBT aligns with your needs hinges on your unique aspirations and the commitment you invest in the process of self-discovery and healing. In the realm of mental well-being, CBT stands as a beacon of empowerment, offering a tailored approach to navigate the complexities of the mind and foster enduring positive transformation.


